The essential role of the masseter muscle is for adequate mastication. This bulky muscle is located laterally to the mandibular ramus and thus plays a vital role in facial aesthetics. Masseter hypertrophy is recognised as an asymptomatic enlargement of one or both masseter muscles. A hypertrophied masseter will alter facial lines, generating discomfort, and create negative cosmetic impacts in many patients. This leads to the prominent mandibular angle which is considered to be aesthetically unacceptable. The muscle function may also be impaired, thus resulting in conditions such as trismus, protrusion, and bruxism.
In most cases of masseter hypertrophy, it is bilateral and symmetric, but asymmetry is not unusual. In the majority of the cases, the etiological factor is unknown; therefore it is considered to be idiopathic. A unilateral occurrence can also be seen when patients chew or clench primarily on one side.

There are various treatment modalities for the management of masseteric hypertrophy. The treatment aims to improve facial balance, change the shape of an overly square face and relief pain or discomfort as a result of an excessively large masseter muscle.
The treatment modalities can be categorised into:
(A) Non-Surgical Treatment for Masseteric Hypertrophy:
Conservative management of the idiopathic masseter hypertrophy includes psychological counselling, use of mouth guards, muscle relaxant, anxiolytic drugs, analgesics, physical therapy, dental restorations, and occlusal adjustments to correct premature contacts. A good result can be achieved in patients with mild hypertrophy, but there is no reliable success rate of isolated clinical therapy. Injection of botulinum toxin type A (Botox) into the masseter muscle was considered as a less invasive modality for the treatment of muscle hypertrophy. Local injection of tiny doses of the Botox into a muscle produces local paralysis, and therefore, specific muscles can be selectively weakened, and atrophy of the muscle occurs. Perhaps the most significant disadvantage of botulinum toxin therapy is that the treatment effect wears away and reverts to the original condition in 4 – 6 months. Unlike surgical excision of muscle tissue that reduces the actual number of muscle cells, botulinum toxin type A only reduces muscle volume temporarily.
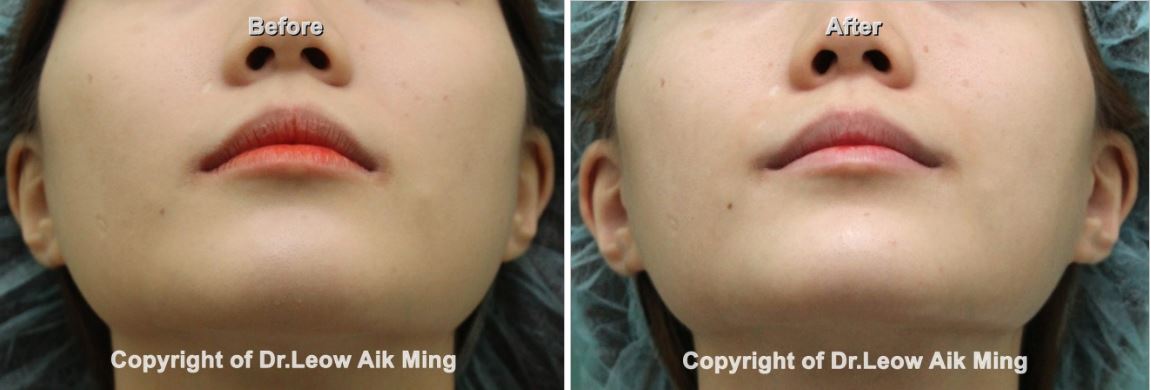
(B) Surgical Treatment for Masseteric Hypertrophy:
This surgical treatment consists of removal of 3/4 to 2/3 of all muscle mass via intraoral approach. Occasionally, mandibular cortical bone or angle osteotomy can also be performed at the same time to achieve a smooth jawline contour. The surgery to access the masseter muscles and the mandible (jawbone) is performed through incisions on the inside of the mouth, between the gum and cheek (lower buccal sulcus area), leaving no visible scarring. Once the correct amount of bone and muscle has been removed, the incision is closed with self-dissolving sutures. The result of a surgical approach to masseteric hypertrophy is predictable and longer lasting compared to the non-surgical method.

Ideal candidates for masseter muscle reduction surgery
- Individual with a positive outlook and specific goals in mind for the improvement of facial appearance.
- Physically healthy with no active or severe pre-existing medical conditions
Preoperative evaluation for masseter muscle reduction surgery:
Communication is vital to achieving the patient’s goals. During the initial consultation, patients will have the opportunity to discuss their goals and desired results with the plastic surgeon. The plastic surgeon will work closely with the patients to reach an agreement about the expectations from the surgical procedures involved and their long term benefits. Every patient is different. Therefore a specific treatment regimen is planned to suit an individual’s need.
- Discussion about patients’ expectations and desired outcome
- Medical conditions, drug allergies and previous medical or surgical treatment
- Use of current medications, vitamins, herbal supplements, alcohol, tobacco and drugs
- Previous surgeries
- Examination of the face and its soft tissues
- Radiological assessment (CT scan of a face) if necessary
- Preoperative evaluation for general anaesthesia
- Photography for preoperative and postoperative evaluation
Preparation for masseter muscle reduction surgery
- Blood investigations or a medical evaluation
- Avoid certain medications or adjust your current medications
- Stop smoking or alcohol well in advance of surgery, (2-3 weeks before the surgery)
- Avoid taking aspirin and certain anti-inflammatory drugs and herbal supplements as they can increase bleeding
The risks and safety information on masseter muscle reduction surgery
It is essential for patients to understand that every surgical procedure has its complications and risks involved. However, if a patient is appropriately assessed before the surgery and postoperative care is given adequately, these risks can be eliminated or reduced. The risks involved in masseter muscle reduction surgery are:
- Bleeding
- Blood clot
- Infection
- Bruises and swelling
- Injury to the surrounding nerves, blood vessels, muscles or bones
- Changes in the skin sensation at the lower lip (temporary)
- Asymmetry
- Anaesthesia risks
- Possibility of revision surgery
Postoperative expectations:
Following masseter muscle reduction surgery, drains (tubes to remove excess blood) may be removed after the second postoperative day. During the initial healing phase, the patient may experience pain, numbness, bruises and swelling around the cheek and lower jaw areas. These symptoms usually fade away after 3-4 weeks. Oral antibiotics and analgesics will be prescribed to reduce the risk of infection and postoperative pain respectively.
Postoperative care:
- Follow the postoperative instructions given carefully
- Head elevation especially when sleeping for 3-4 weeks
- Take the prescribed medications as instructed
- Cold compressive dressing around the lower jaw might be used for 3-7 days
- Regular mouth wash or rinse after every meal if there are any oral wounds
- Soft diet for 2-3 weeks
- Avoid strenuous physical activities for 3-4 weeks
How much will a masseter muscle reduction surgery cost?
Cost is always a consideration in elective surgery. The cost of masseter muscle reduction surgery can vary widely. Cost may include:
- Surgeon’s fee
- Hospital or surgical facility costs
- Medical tests (blood and radiological investigations)
- Anaesthesia fees
- Prescriptions for medication
Masseter muscle reduction surgery is a cosmetic surgical procedure. Therefore, most of the health insurance companies do not cover cosmetic surgeries or their complications.
